Key Takeaways
- National nonresidential construction spending down 0.5% in June 2022.
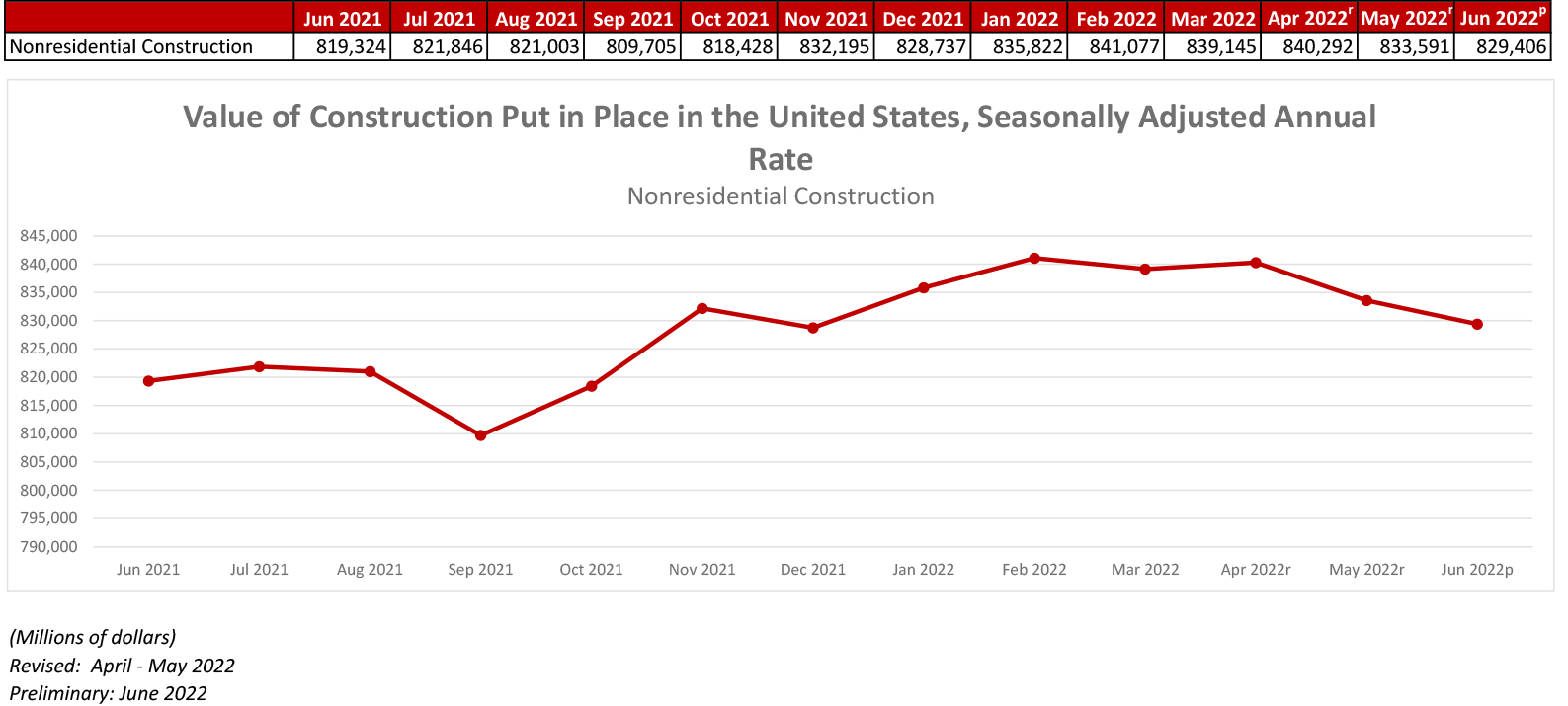
- On a seasonally adjusted annualized basis, nonresidential spending totaled $829.4 billion for the month.
- "For now, many contractors remain busy and continue to operate at or near capacity. Whether that will continue for another 12 to 18 months remains an unanswered question."
Nonresidential Construction Spending Falls 0.5% in June, Says ABC
WASHINGTON, Aug. 1—National nonresidential construction spending was down by 0.5% in June, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data published today by the U.S. Census Bureau. On a seasonally adjusted annualized basis, nonresidential spending totaled $829.4 billion for the month.
Spending was down on a monthly basis in eight of the 16 nonresidential subcategories. Both private and public nonresidential spending fell by 0.5% in June.
“There continues to be significant downward pressure on nonresidential construction spending volumes, and that is likely to intensify going forward,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “To date, construction spending measured in dollars has been propped up by elevated construction delivery costs, including higher materials prices and rapidly rising wages. Despite those inflationary pressures, aggregate nonresidential construction spending has failed to recover to pre-pandemic levels in nominal terms. The situation looks even worse when adjusting for inflation.
“The primary issue is that those high construction delivery charges are inducing a significant fraction of project owners to reconsider start dates,” said Basu. “True, backlog remains elevated, according to ABC’s Construction Backlog Indicator, but this may be because it is taking longer to complete projects. Additional project delays and cancellations are likely as borrowing costs continue to ratchet higher for those who purchase construction services and as the risk of recession increases. For now, many contractors remain busy and continue to operate at or near capacity. Whether that will continue for another 12 to 18 months remains an unanswered question.”
Press Release from Associated General Contractors of America: Construction Spending Falls in June with Declines in Residential and Nonresidential Activity Amid Growing Labor and Materials Shortages
Construction Association Official Says Supply Chain Challenges and Lack of Workers is Suppressing Demand for New Construction Amid Higher Construction Costs and Longer Schedules
WASHINGTON, August 1—Total construction spending fell by 1.1 percent in June as spending on new housing and nonresidential projects declined compared to May, according to an analysis the Associated General Contractors of America released today of federal spending data. Association officials said that the construction spending figures are being impacted as materials and labor shortages are slowing schedules and increasing the cost of construction.
“Strong demand for construction is being offset by rising materials prices and labor shortages,” said Stephen E. Sandherr, the association’s chief executive officer. “As firms stretch schedules and boost costs to cover rising materials prices it is getting harder for public and private owners to proceed with some planned projects.”
Construction spending, not adjusted for inflation, totaled $1.76 trillion at a seasonally adjusted annual rate in June. That figure was 1.1 percent below the upwardly revised May rate and 8.3 percent higher than in June 2021. Private nonresidential construction spending declined for the fourth month in a row, slipping 0.5 percent from May, although the June rate was 1.7 percent higher than in June 2021.
Public construction spending decreased for the second-straight month, falling 0.5 percent from May but was up 0.4 percent from the year-ago rate. Residential spending fell by 1.6 percent for the month, but it up 15.4 percent compared to last June.
The downturn in nonresidential construction spending was widespread. The largest segment, power—comprising electric, oil, and gas projects—slipped 1.7 percent in June. Spending on commercial construction—warehouse, retail, and farm projects—declined 0.5 percent. Educational construction spending decreased 0.5 percent. Among the five largest segments, only manufacturing construction did not fall, but was unchanged from the prior month.
Association officials urged public leaders to boost investments in training programs that expose new and transitioning workers to high-paying construction career opportunities. And they urged officials at all levels of government to work together to address port backups, shipping shortages and manufacturing challenges that are taxing every point of the construction material supply chain.
“Attracting more people into construction careers and fixing the broken supply chain for key materials will help kick start a number of stalled construction projects,” Sandherr said. “In other words, addressing labor and materials shortages is the best way to boost construction spending.”













